
CipherBFT
High-Performance BFT Consensus Engine
First Open-Source Implementation of Autobahn BFT
Decoupling Data Availability from Transaction Ordering to achieve both high throughput of DAG and low latency of PBFT.
Why High-Performance L1?
L2 Sequencer Centralization Problem
L2 Limitations
Most L2s use a single sequencer. This creates fundamental vulnerabilities in censorship resistance and liveness. Single point of failure.
Multi-Proposer L1 Advantage
Validators distributed across regions can receive transactions simultaneously. Structurally faster inclusion than single sequencer. True decentralization.
Why Latency Matters
In DeFi, latency is a functional requirement. In arbitrage, hundreds of milliseconds separate profit from loss. In liquidations, delays cause protocol losses due to insufficient collateral. This is not about convenience - it is about whether the system works or not.
From PBFT to DAG
The Evolution of BFT Consensus
PBFT (1999)
Leader proposes, 3-phase voting. Problem: O(n^2) message complexity.
DAG-based (2021+)
Narwhal, Bullshark - separate data propagation from ordering. Narwhal-HotStuff achieved 130K TPS. But complex commit rules increase latency. Bullshark requires up to 12 message delays.
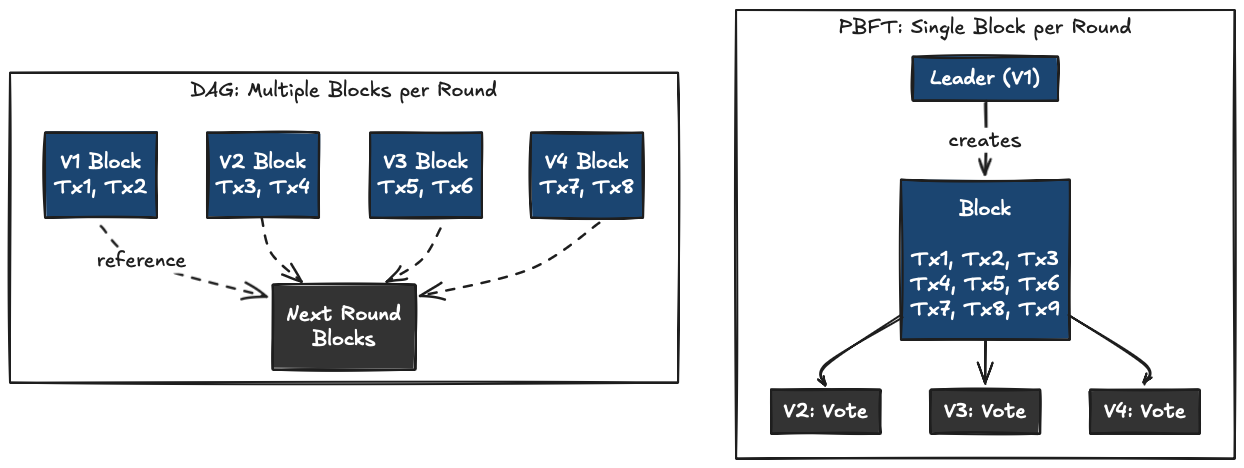
The DAG Problem
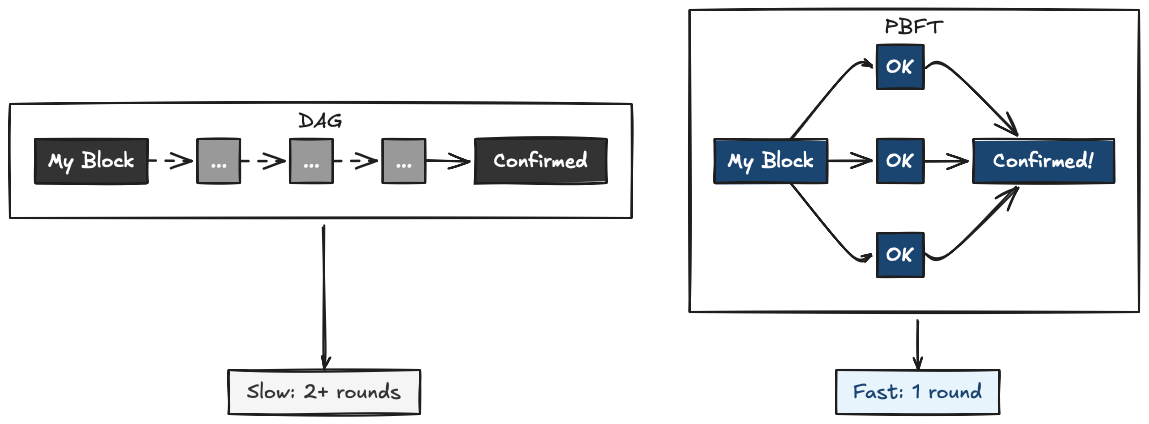
DAG protocols must wait for references to accumulate across multiple rounds before committing. This waiting time is what Autobahn eliminates.
Autobahn BFT
Published at SOSP 2024
The Key Insight
Separate Data Dissemination Layer and Consensus Layer.
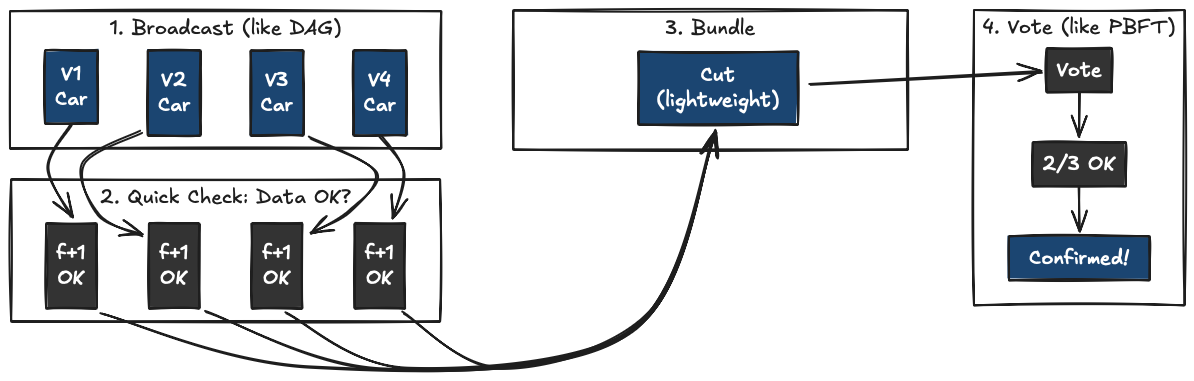
- Data Dissemination: All validators broadcast data simultaneously. Each creates blocks in their own Lane, collects f+1 attestations to create Proof of Availability.
- Consensus: Leader periodically proposes a Cut (snapshot of Lanes). 2-round PBFT-style consensus. Fast path commits in 3 message delays.
Why is it fast?
Traditional DAG uses Reliable Broadcast - heavy. Autobahn uses best-effort broadcast with lightweight PoA. Data availability is separated from consensus critical path. Consensus only votes on metadata (Cut), not full transactions.
CipherBFT Architecture
3-Layer Modular Design
Key Design Decisions
BLS12-381 for DCL
Signature aggregation - multiple attestations combined into one. Reduces communication cost.
Ed25519 for CL
Fast individual verification. Consensus messages need quick verification over aggregation.
Malachite BFT
Rust implementation of Tendermint by Informal Systems. Formally verified, modular design.
Pipelining
Parallel processing of different heights. Height N executes while N+1 reaches consensus while N+2 propagates data.
Research Collaboration
CipherBFT is a joint research initiative combining academic excellence with industry expertise
Decipher
Academic ResearchThe leading blockchain research group at Seoul National University. Bringing cutting-edge research capabilities and academic rigor to the project.
Visit WebsiteB-Harvest
Research & DevelopmentA blockchain research and infrastructure company since 2018. Deep expertise in BFT consensus mechanisms and the Cosmos ecosystem.
Visit Website